Flange gasket
Flange gasket: Everything you need to know
Flange gaskets are an indispensable component in many industrial applications. They are used to seal the joints between two flanges to prevent liquids or gases from escaping.
The history of flange gaskets goes back a long way and reflects the development of the industrial revolution. Originally made from simple materials such as hemp, they have developed into highly sophisticated components with specific properties for various applications.
The function of flange gaskets is to ensure the integrity of piping systems. They play a key role in industries such as petrochemicals, mechanical engineering and power plants.
A crucial aspect of flange gaskets is their ability to withstand different pressure levels, chemical properties of the transported media and temperature conditions.
Important facts:
- Variety of materials: Modern flange gaskets are made from a variety of materials including rubber, plastic, metal and special composite materials.
- Areas of application: They are used in many branches of industry, from water and waste water treatment to aerospace technology.
- Safety relevance: Their importance for safety in industrial plants cannot be overestimated.
Due to their versatility and importance, flange gaskets are a fascinating subject that requires an in-depth understanding of their selection, application and maintenance.
REQUEST O-RINGS QUICKLY AND EASILY?
Almost any dimension available
Offer received in record time
No minimum order quantities or minimum item values
One contact for all concerns
#1 Flange gasket - basics and importance
Flange gaskets, essential components in numerous industrial sectors, play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and safety of piping systems.
These gaskets, which are fitted between two flanges, prevent the escape of liquids and gases, thus fulfilling a critical function in various applications.
History and development
The development of flange gaskets is closely linked to the progress of industrial technologies.
Originally made from simple materials such as hemp, they have evolved over time into complex and highly specialized components that can be made from a variety of materials.
Function and meaning
The main function of a flange gasket is to create a secure and tight connection between two pipe flanges.
This is particularly important in industries where safety and reliability are top priorities, such as petrochemicals, mechanical engineering and power plants.
Flange gaskets must be able to withstand various environmental conditions such as pressure, temperature and chemical stress.
Versatile applications
Flange gaskets are used in a wide range of applications, from water and wastewater treatment to aerospace. Their flexibility and adaptability to different conditions make them an indispensable component in many technical systems.
Safety aspect
The safety relevance of flange gaskets cannot be emphasized enough. They are crucial for preventing leaks, which can lead to environmental damage, operational downtime and, in extreme cases, serious accidents.
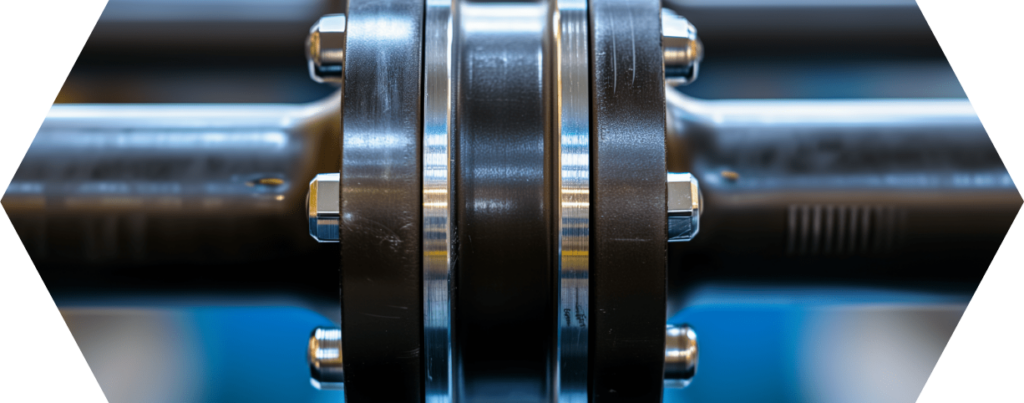

#2 Different types of flange gaskets and their properties
The world of flange gaskets is diverse and complex. Various types of seals are developed to meet specific requirements in different areas of application.
Here we will look at the most common types of flange gaskets and their unique properties.
Metallic vs. non-metallic flange gaskets
- Metallic seals: Often made of steel, stainless steel or other metals. They are ideal for extremely high pressure and temperature conditions and are often used in the petrochemical industry and in power plant construction.
- Non-metallic seals: Made from materials such as rubber, PTFE or graphite. They are more flexible and better suited to lower pressure and temperature ranges. Common applications can be found in the food industry and water treatment.
Spiral wound seals
- Properties: Consist of a metallic winding strip and a softer filling material, often made of graphite or PTFE.
- Application: Ideal for flange connections that are subject to regular pressure fluctuations and thermal cycles, such as in oil and gas pipelines.
Rubber and plastic seals
- Rubber seals: Often made of nitrile, neoprene or EPDM. They offer good elasticity and are resistant to many chemicals and liquids.
- Plastic seals: PTFE gaskets are known for their excellent chemical resistance and are used in the chemical industry.
Comparison and areas of application
- Metal seals are generally more durable and more resistant to extreme conditions, but also more cost-intensive.
- Non-metallic gaskets offer more flexibility and a better seal at lower pressures, but may not be suitable for all applications.
| Seal type | Pressure range | Temperature range | Cost range | Areas of application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic | High | High | Higher | Petrochemicals, power plants |
| Non-metallic | Low | Low to medium | Lower | Food industry, water treatment |
| Spiral wound | Medium to high | Medium to high | Medium to High | Oil and gas industry |
| Rubber | Low | Low to medium | Lower | General industry |
| Plastic | Low to medium | Medium | Medium | Chemical industry |

#3 Selection criteria for the perfect flange gasket
Selecting the right flange gasket is crucial for the safety and efficiency of industrial systems.
There are several factors that need to be considered when selecting a flange gasket to ensure that it is the best fit for the requirements of the application.
Material selection and chemical resistance
- Materials: The choice of the right material depends on the type of liquids or gases that are transported in the pipelines. For example, corrosive chemicals require a seal with high chemical resistance, such as PTFE.
- Chemical resistance: The seal must be resistant to the specific chemicals with which it comes into contact in order to prevent corrosion and material degradation.
Temperature and pressure resistance
- Temperature range: The seal must be suitable for the operating temperature range of the application. High-temperature applications, for example, require metallic or special high-temperature seals.
- Pressure range: The maximum pressure load to which the seal is exposed determines the choice of seal type. High-pressure applications require more robust, often metallic seals.
Flange type and size
- Flange compatibility: The gasket must exactly match the flange type and its size. This includes consideration of the flange geometry, bolt distribution and gasket fit.
- Sizing: Correct sizing is essential for sealing efficiency. A seal that is too large or too small can lead to leaks.
Checklist for the selection
- Determine the chemical compatibility: Make sure that the sealing material is compatible with the transported media.
- Determine the required temperature and pressure range: Select a seal that can withstand the operating conditions.
- Check the flange specifications: Ensure the exact fit and size for your specific flange.
- Take the ambient conditions into account: Ensure that the seal remains functional even under the prevailing ambient conditions.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that you select the optimum flange gasket for your specific requirements. The right choice contributes significantly to the safety, efficiency and longevity of your systems.
| Seal type | Materials | Temperature range | Pressure resistance | Costs | Main applications | Special properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic seals | Steel, stainless steel, other metals | Very high (up to 1,000°C) | Very high (over 250 bar) | Higher | Petrochemicals, power plants, high-temperature plants | High strength, durability, suitable for extreme conditions |
| Non-metallic seals | Rubber, PTFE, graphite | Low to medium (up to 250°C) | Low to medium (up to 100 bar) | Lower | Food industry, water treatment, general industry | Flexibility, good chemical resistance, cost-efficient |
| Spiral wound seals | Metallic winding strip, graphite/PTFE filling material | Medium to high (up to 700°C) | Medium to high (up to 200 bar) | Medium | Oil and gas industry, power generation, heavy industry | Adaptable to pressure fluctuations, robust, versatile applications |
| Rubber seals | Nitrile, neoprene, EPDM | Low to medium (up to 150°C) | Low (up to 25 bar) | Lower | Sanitary, HVAC, vehicle construction | Elasticity, good sealing at low pressure, weather resistance |
| Plastic seals (e.g. PTFE) | PTFE, Teflon | Low to high (up to 260°C) | Low to medium (up to 100 bar) | Medium | Chemical industry, pharmaceutical industry | Excellent chemical resistance, low friction, temperature resistant |
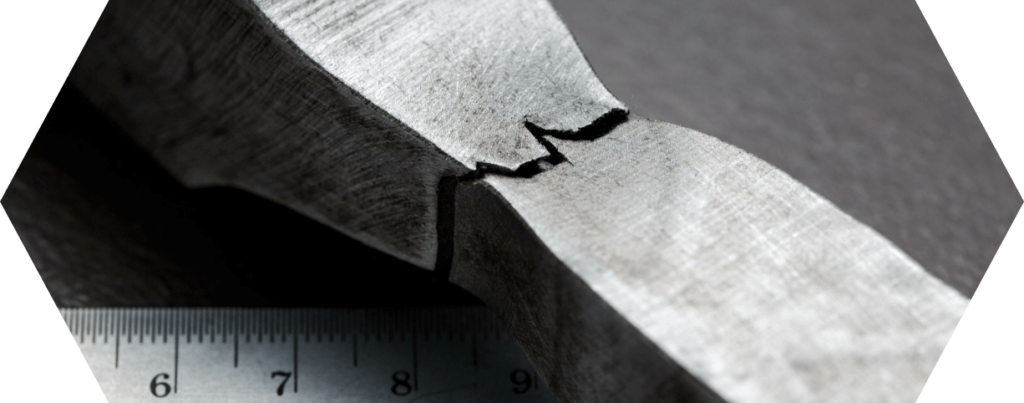

#4 Instructions for the installation and maintenance of flange gaskets
Correct installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensure the functionality and longevity of flange gaskets.
In this chapter, we will look at the best practices for installing and maintaining these important components.
Step-by-step assembly instructions
- Flange preparation: Clean the flange surfaces thoroughly to ensure that no residues or impurities can affect the gasket.
- Check the gasket: Make sure that the gasket is undamaged and suitable for the specific flange type and application conditions.
- Positioning the gasket: Place the gasket carefully on the flange to ensure correct alignment.
- Tightening the flange bolts: Tighten the bolts in a criss-cross sequence and in accordance with the specified torque specifications.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
- Excessive tightening: Can lead to damage to the seal. Always follow the recommended torque specifications.
- Use of damaged seals: Even minor damage can impair the sealing performance. Only use seals that are in perfect condition.
- Ignore flange defects: Damaged or distorted flanges can impair the effectiveness of the gasket. Flanges must be checked before installation and replaced or repaired if necessary.
Maintenance and inspection tips
- Regular inspections: Check the seals regularly for signs of wear, damage or leaks.
- Environmental conditions: Consider changes in operating conditions that could affect the seals, such as temperature fluctuations or chemical exposure.
- Replacement intervals: Plan regular maintenance intervals to replace the seals when necessary, especially in critical applications.
Service life and replacement intervals
The service life of a flange gasket depends on many factors, including the material, operating conditions and maintenance.
It is important to maintain a regular maintenance schedule and to replace the seals at the first sign of wear or damage.
The proper installation and maintenance of flange gaskets are crucial for the safety and efficiency of industrial plants.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the reliability of your system and extend its service life.

#5 Anleitung zur Montage und Wartung von Flanschdichtungen
Eine korrekte Montage und regelmäßige Wartung sind entscheidend, um die Funktionsfähigkeit und Langlebigkeit von Flanschdichtungen zu gewährleisten.
In diesem Kapitel werden wir uns mit den besten Praktiken für die Installation und Pflege dieser wichtigen Komponenten befassen.
Richtige Anziehreihenfolge
- Eine kreuzweise Anziehreihenfolge ist wichtig, um eine gleichmäßige Verteilung des Drucks über die gesamte Dichtung zu gewährleisten.
- Tipp: Beginnen Sie mit der Schraube in der 12-Uhr-Position, gehen Sie dann zur 6-Uhr-Position, gefolgt von 3 Uhr und 9 Uhr. Fahren Sie in diesem Muster fort, bis alle Schrauben angezogen sind.
Vermeidung von Übermäßigem Anziehen
- Übermäßiges Anziehen der Schrauben kann die Dichtung beschädigen, ihre Lebensdauer verkürzen und sogar zu Leckagen führen. Dies passiert, weil der übermäßige Druck das Material der Dichtung übermäßig komprimiert oder verformt.
- Tipp: Verwenden Sie ein Drehmomentschlüssel, um die Schrauben mit dem vom Hersteller empfohlenen Drehmoment anzuziehen. Dies stellt sicher, dass Sie genau den richtigen Druck ausüben.
Schrauben und Ihre Drehmomente für Flanschdichtungen
Diese Tabelle bietet eine Orientierungshilfe für die gängigen Schraubengrößen und ihre entsprechenden Drehmomente bei der Montage von Flanschdichtungen.
Die Werte können je nach Material der Schrauben und der spezifischen Anwendungsbedingungen variieren. Es ist ratsam, die Herstellerangaben für genaue Spezifikationen zu konsultieren.
| Schraubengröße | Drehmoment für Stahlschrauben | Drehmoment für Edelstahlschrauben |
|---|---|---|
| M8 (8mm) | 20 – 25 Nm | 15 – 20 Nm |
| M10 (10mm) | 40 – 50 Nm | 30 – 40 Nm |
| M12 (12mm) | 70 – 85 Nm | 55 – 70 Nm |
| M16 (16mm) | 160 – 200 Nm | 120 – 160 Nm |
| M20 (20mm) | 300 – 350 Nm | 230 – 280 Nm |
| M24 (24mm) | 450 – 500 Nm | 340 – 380 Nm |
| M30 (30mm) | 800 – 900 Nm | 600 – 700 Nm |
Hinweise:
- Material der Schrauben: Die Drehmomente variieren je nach Material. Stahlschrauben können in der Regel höhere Drehmomente aufnehmen als Edelstahlschrauben.
- Anwendungsbedingungen: Die angegebenen Werte sind allgemeine Richtlinien. Spezifische Anwendungen, wie hohe Temperaturen oder korrosive Umgebungen, können andere Drehmomente erfordern.
- Dichtungsmaterial: Beachten Sie auch das Material der Flanschdichtung, da einige Materialien empfindlicher auf Druck reagieren und ein angepasstes Drehmoment benötigen.
- Herstellerangaben: Immer die Empfehlungen des Dichtungs- und Schraubenherstellers beachten, um die optimale Leistung und Sicherheit zu gewährleisten.

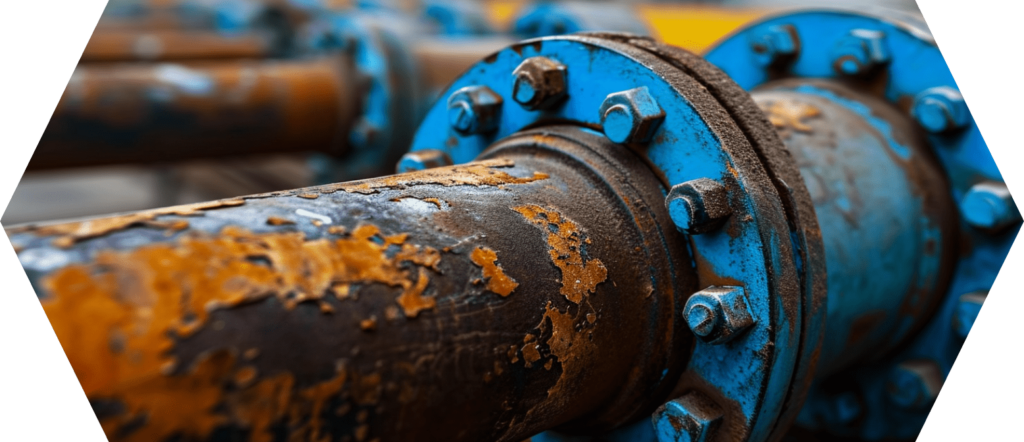
#5 Problems and solutions when using flange gaskets
Flange gaskets are crucial components in many industrial systems, and their correct functioning is essential for operational safety.
Nevertheless, various problems can occur in the course of their use. In this chapter, we will look at some common problems and point out solutions.
Leaks and their causes
- Causes of leaks: These can occur for a number of reasons, such as uneven flange surfaces, incorrect tightening of bolts, gasket wear or unsuitable gasket selection.
- Solutions: Ensure flanges are level and clean, tighten bolts evenly and to the correct torque, and select the correct gasket for the specific operating conditions.
Corrosion and material fatigue
- Corrosion: Chemical reactions, especially in aggressive environments, can lead to corrosion of the seal.
- Material fatigue: Long-term loads and temperature fluctuations can cause the material to fatigue.
- Countermeasures: Choose materials that are suitable for the chemical and physical conditions and carry out regular inspections to detect early signs of wear or damage.
Correction of installation errors
- Common installation errors: These include incorrect alignment of the gasket, insufficient bolt preload and the use of incompatible gasket materials.
- Corrective action: Check gasket alignment during installation, ensure bolts are tightened evenly and use materials suitable for the specific application requirements.
By understanding these common problems and their solutions, professionals can improve the performance and reliability of their flange sealing systems and reduce the likelihood of operational failures and safety risks.

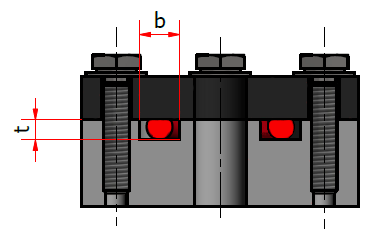
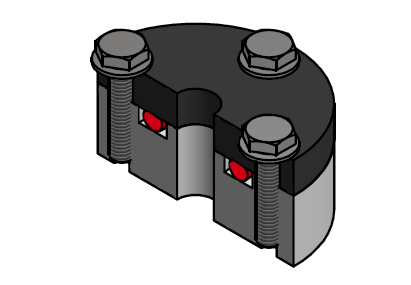
#7 Einsatz von O-Ringen als Flanschdichtung
O-Ringe sind eine beliebte Art von Dichtungen, die in verschiedenen Anwendungen eingesetzt werden, einschließlich als Flanschdichtungen.
Sie unterscheiden sich in Design und Anwendungsbereich von Flachdichtungen. Hier sind die Gründe für die Verwendung von O-Ringen, die Unterschiede zu Flachdichtungen sowie deren Vor- und Nachteile:
Warum werden O-Ringe verwendet?
- Flexibilität und Vielseitigkeit: O-Ringe können sich an verschiedene Oberflächen und Formen anpassen.
- Kosteneffizienz: Sie sind in der Regel kostengünstiger in der Herstellung und im Einsatz als viele andere Dichtungstypen.
- Einfache Installation und Wartung: O-Ringe sind einfach zu installieren und erfordern wenig Wartung.
- Zuverlässigkeit: Bieten eine effektive Abdichtung bei einer Vielzahl von Druck-, Temperatur- und Medienbedingungen.
Wann verwendet man Flachdichtungen und wann O-Ringe?
- Flachdichtungen:
- Einsatz bei größeren Flanschverbindungen, insbesondere wenn eine größere Dichtungsfläche benötigt wird.
- Geeignet für Anwendungen, in denen die Dichtungen hohen Drücken und Temperaturen ausgesetzt sind.
- Oft verwendet in Industrieanlagen und in der Petrochemie.
- O-Ringe:
- Einsatz in kleineren oder komplex geformten Anwendungen, wo eine kompakte und flexible Dichtung benötigt wird.
- Ideal für dynamische Anwendungen, bei denen sich Teile relativ zueinander bewegen.
- Häufig in der Automobilindustrie, in hydraulischen/pneumatischen Systemen und in der Konsumgüterelektronik.
Vor- und Nachteile
O-Ringe
- Vorteile:
- Hohe Dichtigkeit bei einer Vielzahl von Anwendungen.
- Widerstandsfähig gegen viele Chemikalien und Temperaturveränderungen.
- Einfache Montage und geringer Platzbedarf.
- Nachteile:
- Nicht ideal für Anwendungen mit extrem hohen Drücken oder Temperaturen.
- Kann durch scharfe Kanten oder raue Oberflächen beschädigt werden.
- Erfordert präzise Nutabmessungen und Oberflächengüte.
Flachdichtungen
- Vorteile:
- Geeignet für hohe Drücke und Temperaturen.
- Kann größere Unregelmäßigkeiten in den Flanschoberflächen ausgleichen.
- Vielfältige Materialauswahl für unterschiedliche Anforderungen.
- Nachteile:
- Kann komplizierter in der Montage sein.
- Größerer Platzbedarf und potenziell höhere Kosten.
- Kann bei unsachgemäßer Anwendung zu Leckagen führen.
Zusammenfassend hängt die Wahl zwischen O-Ringen und Flachdichtungen von den spezifischen Anforderungen der Anwendung ab, einschließlich Größe, Druck, Temperatur und der Art der Flüssigkeiten oder Gase, die abgedichtet werden sollen.
O-Ringe bieten eine effiziente Lösung für viele Standardanwendungen, während Flachdichtungen für anspruchsvollere, industrielle Anwendungen besser geeignet sein können.

#6 Future trends and innovations in flange gasket technology
Flange gasket technology is constantly evolving, driven by the need for greater efficiency, safety and environmental compatibility.
In this chapter, we take a look at future trends and innovations in this area.
New materials and production techniques
- Innovative materials: Research is focusing on the development of new materials that have higher temperature and pressure tolerances and are also more chemically resistant.
- Manufacturing techniques: Advances in manufacturing technology, such as 3D printing, are enabling more precise and customizable gasket designs.
Sustainability and environmental impact
- Environmentally friendly materials: A growing trend is the use of more environmentally friendly materials that are less harmful to the environment and are easier to dispose of or recycle at the end of their service life.
- Energy efficiency: The development of seals that help to reduce energy consumption in industrial plants is becoming increasingly important.
Industry 4.0 and flange gaskets
- Smart seals: The focus is on integrating sensors into seals that provide real-time data on their condition and operating conditions. This technology enables predictive maintenance and increases overall operational reliability.
- Automation: Automated inspection and maintenance systems for seals can help to reduce human error and increase efficiency.
Outlook and sector development
- Collaboration: Collaboration between manufacturers, research institutions and end users is crucial to drive the development of more effective and environmentally friendly sealing solutions.
- Adapting to change: The ability to adapt quickly to new challenges and technological advances is becoming increasingly important for manufacturers and users of flange gaskets.
Future developments in flange gasket technology promise not only improved performance and reliability, but also a stronger focus on sustainability and integration into intelligent industrial systems.
These innovations will significantly change the way we handle these crucial components in industrial applications.

#7 FAQ section: Flange gasket
Finally, some answers to frequently asked questions.
#7.1 What is a flange gasket and what is it used for?
A flange gasket is a special gasket that is used between two flanges in piping systems to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
They are indispensable in many industries, such as petrochemicals, mechanical engineering and power plants, to maintain the integrity of systems by preventing the escape of liquids or gases.
#7.2 What materials are used for flange gaskets?
Flange gaskets are made from a variety of materials, including rubber, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), metals such as steel and stainless steel, as well as special composite materials.
The choice of material depends on the specific application, including the temperature and pressure conditions as well as the chemical compatibility with the transported media.
#7.3 How to choose the right flange gasket?
Selecting the right flange gasket requires consideration of several factors: the material, which must be compatible with the transported media, the temperature and pressure range of the application, the flange size and type as well as the operating conditions.
Correct selection ensures efficient and safe operation of the piping system.
#7.4 How important is the maintenance of flange gaskets?
The maintenance of flange gaskets is crucial for the longevity and safety of piping systems.
Regular inspections help to detect wear, damage or leaks at an early stage. Maintenance includes checking the condition of the flanges, tightening the screws evenly and replacing the gasket if necessary.
#7.5 What role do spiral wound seals play in the industry?
Spiral wound gaskets, consisting of a metallic winding strip and a softer filler material, are particularly important in industries that work with high pressures and temperatures, such as the oil and gas industry.
They offer excellent adaptability to changing operating conditions and are known for their reliability under regular pressure fluctuations.
#7.6 How is flange gasket technology developing?
Flange gasket technology is constantly evolving, with a focus on new materials, improved manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing, sustainability and integration into smart industrial systems.
Innovations such as smart seals with integrated sensors provide real-time data and enable predictive maintenance, which increases the safety and efficiency of industrial plants.
#9.7 Wer sind drei Hersteller von Flachdichtungen und Zuschnitten aus Deutschland?
#9.8 Was ist der Unterschied zwischen Flanschdichtung, Kolbendichtung und Stangendichtung?
Flanschdichtung
- Verwendungszweck: Flanschdichtungen werden verwendet, um die Verbindungsstelle zwischen zwei Flanschen in Rohrleitungssystemen abzudichten.
- Funktion: Sie verhindern das Austreten von Flüssigkeiten oder Gasen an der Verbindungsstelle.
- Eigenschaften: Diese Dichtungen müssen Druck, Temperaturschwankungen und manchmal korrosiven Umgebungen standhalten können. Sie können aus verschiedenen Materialien wie Gummi, PTFE, Metall oder Graphit bestehen.
- Einsatzgebiete: Verwendung in vielfältigen Industrien wie Öl- und Gas, Petrochemie, Wasserbehandlung und in der Lebensmittelindustrie.
Kolbendichtung
- Verwendungszweck: Kolbendichtungen sind in hydraulischen oder pneumatischen Zylindern zu finden. Sie dichten den Raum zwischen dem Zylindergehäuse und dem beweglichen Kolben ab.
- Funktion: Sie verhindern das Durchsickern von Flüssigkeit (Hydrauliköl, Luft) von einer Seite des Kolbens auf die andere und ermöglichen so eine effektive Kraftübertragung.
- Eigenschaften: Diese Dichtungen müssen widerstandsfähig gegenüber Druck, Abrieb und gegebenenfalls hohen Temperaturen sein. Oft aus Elastomeren, PTFE oder anderen Polymermaterialien gefertigt.
- Einsatzgebiete: Häufig in Baumaschinen, Automobil-Hydrauliksystemen und in der Fertigungsindustrie.
Stangendichtung
- Verwendungszweck: Stangendichtungen werden in hydraulischen und pneumatischen Zylindern eingesetzt, ähnlich wie Kolbendichtungen, aber sie dichten den Bereich um die Zylinderstange ab.
- Funktion: Verhindern das Austreten von Flüssigkeiten entlang der Zylinderstange nach außen und schützen gleichzeitig den Zylinder vor Verunreinigungen von außen.
- Eigenschaften: Muss Druck, dynamische Bewegung, Abrieb und möglicherweise Umweltfaktoren widerstehen können. Hergestellt aus Materialien wie Polyurethan, Nitrilkautschuk oder PTFE.
- Einsatzgebiete: Einsatz in hydraulischen Pressen, Aufzügen, Landwirtschaftsmaschinen und vielen anderen hydraulisch oder pneumatisch betriebenen Systemen.
“I am convinced that we should share our knowledge with the world. I hope I have been able to answer all your questions. If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us at any time. We will be happy to help you.”

Lord of the O-rings
Author of the poetry academy



