FDA approval
FDA approval: Everything you need to know
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a US authority responsible for monitoring and regulating food, drugs, medical devices, tobacco products and cosmetics.
Its main task is to protect public health by ensuring that these products are safe, effective and correctly labeled. This includes both domestic and imported products.
The FDA was founded in 1927, and its role has evolved over time, particularly in response to various medical crises and scandals.
REQUEST O-RINGS QUICKLY AND EASILY?
Almost any dimension available
Offer received in record time
No minimum order quantities or minimum item values
One contact for all concerns
#1 FDA approval: Basics
FDA approval is a crucial step for the introduction of new drugs and medical devices to the US market.
It ensures that these products meet the authority’s strict safety and efficacy standards. The approval is based on a comprehensive review of the documentation submitted by the manufacturers, which must prove the quality, efficacy and safety of the products.
This includes conducting and evaluating clinical studies, manufacturing according to defined standards and providing detailed information on the composition and mode of action of the product.
The FDA structure includes various centers and offices that specialize in specific product categories, such as the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition.
This structure enables the FDA to respond effectively to the specific challenges and requirements of each product category.
The FDA approval process is known worldwide for its rigor and detail. FDA approval is often considered the gold standard in the pharmaceutical industry as it signals a high level of confidence in the safety and efficacy of a product. The FDA’s decisions often influence regulatory practices in other countries.

#2 FDA approval: The approval process
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process is a complex, multi-step process designed to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical devices and drugs before they are approved for the U.S. market.
Main approval procedure for medical devices
The FDA has various approval processes for medical devices, including:
- Premarket Notification 510(k) (PMN): For products that are substantially equivalent to an existing and approved product.
- Premarket Approval (PMA): This is the most stringent procedure required for Class III medical devices. It involves an in-depth review of safety and efficacy by the FDA.
- Investigational Device Exemption (IDE): Allows the use of an investigational device in clinical trials.
- Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE): For devices intended for the treatment or diagnosis of rare diseases or conditions.
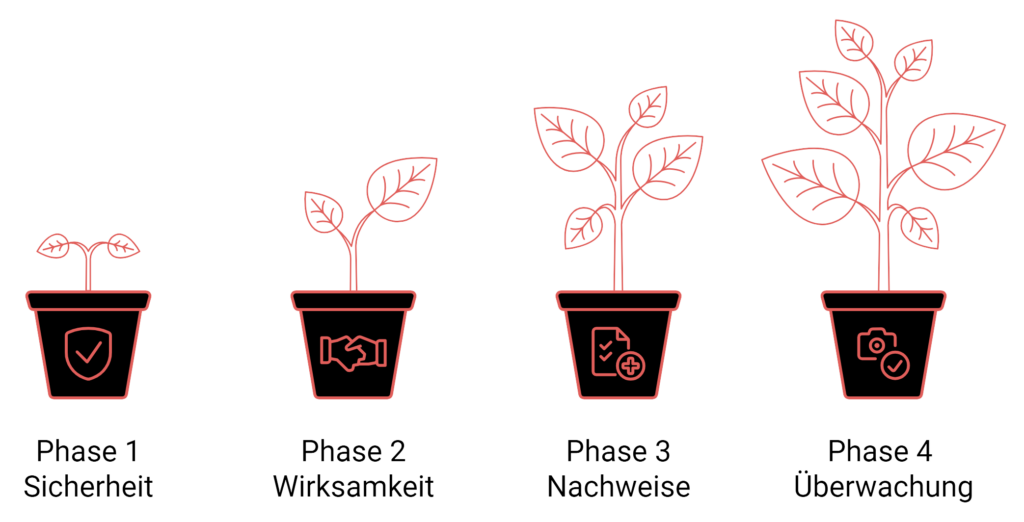
Phases of the drug approval procedure
The authorization procedure for medicinal products comprises several phases:
Phase 1Focuses on safety, involves 20 to 80 healthy volunteers and lasts about a year.
Phase 2Focuses on efficacy. In this phase, approximately 100 to 300 patients are observed over a period of two years.
Phase 3Phase 2 : Begins when proof of efficacy has been provided in phase 2. It comprises several hundred to 3,000 patients and lasts an average of three years.
Phase 4Post-market surveillance for further evaluation of safety and efficacy after approval.
New Drug Application (NDA)
The submission of a New Drug Application (NDA) is a crucial step in which the manufacturer asks the FDA for permission to market its drug on the US market. This application includes extensive data from animal studies and clinical trials as well as information on dosage, side effects and pharmacokinetics.
Special approval programs
The FDA also has special programs to expedite the development and review of certain drugs:
- Fast Track: For drugs that treat serious illnesses and fulfill an unmet medical need.
- Breakthrough Therapy: For drugs that show a significant improvement over existing treatments.
- Priority review: The aim is to decide on an application within six months.
- Accelerated Approval: Can be used for promising therapies that treat a serious or life-threatening condition.

#3 FDA approval: challenges and hurdles
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) offers various types of approvals for drugs, biological products and medical devices. Common application types include:
New Drug Application (NDA)
This application is submitted when a company believes it has gathered sufficient evidence of a new drug’s safety and effectiveness to meet the FDA’s requirements for marketing approval. The NDA must include data from a variety of technical perspectives, including chemistry, pharmacology, medicine, biopharmaceutics and statistics.
Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
This application allows for the review and ultimate approval of a generic drug. Generic drug applications are referred to as “abbreviated” because they typically do not need to include preclinical (animal) and clinical (human) data on safety and efficacy. Instead, the applicant must scientifically demonstrate that their product is bioequivalent (i.e. it works in the same way as the innovator drug).
Investigational New Drug Application (IND)
This is required to obtain an exemption from the statutory requirement that a drug must undergo an approved marketing application before it is transported or distributed across state lines.
Biologics License Application (BLA)
Biological products are approved for marketing under the provisions of the Public Health Service (PHS) Act. A BLA contains specific information about the manufacturing processes, chemistry, pharmacology, clinical pharmacology, and medical effects of the biological product.
Over-the-Counter Drugs (OTC)
OTC medicines can be approved either through an NDA or an OTC monograph procedure. An OTC monograph procedure is essentially a “rule book” for each therapeutic category that establishes conditions such as active ingredients, uses (indications), dosages, labeling and testing under which an OTC drug is generally recognized as safe and effective (GRASE) and can be marketed without an NDA and prior FDA approval.
The approval process for medical devices is similar to that for medicinal products. These devices are classified according to risk, with Class I being the lowest and Class III the highest risk level.

#4 FDA approval: Elastomers and Code of Federal Regulations (CFR)
The provisions of the CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) Title 21 focuses in particular on the regulations relating to elastomers and rubber in the food, beverage and water sectors.
CFR Title 21 and elastomers/rubber
FDA regulations for rubber products that come into contact with food are set forth in CFR Title 21, Chapter 1, Subchapter B, Part 177, Subpart C and Section 2600. These regulations provide guidance on the manufacture and use of elastomers and rubber in products used in the food and beverage industry.
The FDA divides food into two categories when it comes to compatibility with rubber:
Class I: This category includes foods such as edible oils, butter, milk and dairy products as well as cooking oils. Rubber compounds that meet these requirements are also compatible with Class II foods.
Class II: This category refers to foods that do not contain edible oils or dairy products, such as water, soft drinks, alcoholic beverages and other aqueous solutions.
FDA 21 CFR 177.2600
The 21 CFR 177.2600 regulation is essentially a list of approved base elastomers and vulcanization materials.
These materials are used in rubber production and are considered safe. Products that comply with these guidelines are used in applications such as gaskets, worktops, non-slip pads and shielding in food processing.
They are also found in butchers, pharmaceutical processing plants, commercial kitchens, hospitals, food processing plants, the cosmetics industry, industrial plants and grocery stores.
Common O-ring materials with FDA approval are FFKM, EPDM, FKM, PTFE, FEP, VMQ AND FVMQ.

#5 FDA approval: future and conclusion
The future of the FDA approval process looks set for some important developments:
Improved processes for drug approval and monitoring
The FDA has improved its drug approval processes, helping to ensure that patients have faster access to effective medications while minimizing the risk of drug side effects.
New laws to improve the approval process
Laws such as the FDA Safety and Innovation Act (FDASIA) of 2013 were enacted to improve the approval process and expand access to new drugs.
Increased efficiency and cost reduction
By shortening the median approval time for new molecular drugs from 19 to 10 months and introducing new laws, the FDA aims to make the process more efficient
Continuous improvement and collaboration
The FDA strives to continuously improve its processes and collaborates with various organizations to develop safe and effective medicines for patients.
#6 FDA approval: More questions answered
In the following chapter we will answer further questions on the subject of FDA approval.
#6.1 FDA approval for medical devices
FDA approval is crucial for the safety and efficacy of medical devices.
It guarantees that products have undergone rigorous testing before being placed on the market, which is important for patients and manufacturers alike.
#6.2 FDA approval in Germany
FDA approval also plays an important role in Germany, especially for companies that want to launch their medical devices and drugs on the US market.
It symbolizes high safety and quality standards, which strengthens confidence in these products.
“I am convinced that we should share our knowledge with the world. I hope I have been able to answer all your questions. If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us at any time. We will be happy to help you.”

Lord of the O-rings
Author of the Sealing Academy
